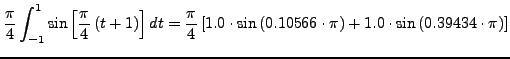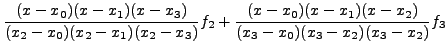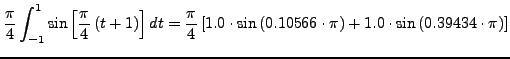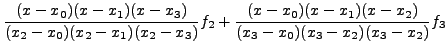Next: Γενίκευση της μεθόδου Gauss
Up: Μέθοδος Gauss-Legendre
Previous: Μέθοδος Gauss-Legendre
Contents
Index
Θα εφαρμόσουμε τη μέθοδο Gaussγια 4 σημεία:
Αντίστοιχα, η μέθοδος Simpsonμε 32 σημεία σημεία δίνει:
1.0000003 και για 64 σημεία: 9.99999983.
Kostas Kokkotas
2005-06-13